The darbuka, also known as the darabuka or darbuka, is a traditional Middle Eastern percussion instrument that has been a staple in Arabic and Turkish music for centuries. Despite their similarities, there are distinct differences between the Arabic and Turkish darbuka that set them apart from one another. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the unique characteristics of each type of darbuka, their history, and how they are used in music. Whether you’re a seasoned musician or just starting out, this guide will provide you with a deep understanding of the differences between Arabic and Turkish darbuka and how they are used in modern music. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of darbuka!
What is a Darbuka?
Origins of the Darbuka
The darbuka, also known as the darabouka or darbuka, is a type of drum that is commonly used in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean music. The origins of the darbuka can be traced back to ancient Egypt, where archaeological evidence suggests that drums were used in religious ceremonies and for other purposes.
The darbuka has undergone several changes over the centuries, and its design and construction have been influenced by various cultures. For example, the Turkish darbuka is typically made from clay or copper, while the Arabic darbuka is often made from wood or plastic.
One of the most significant differences between the Arabic and Turkish darbuka is the way they are played. Arabic darbuka players often use a variety of techniques, such as the “riff” and the “dumbek beat,” to create complex rhythms and patterns. Turkish darbuka players, on the other hand, tend to focus on a simpler, more straightforward style of playing.
Despite these differences, both the Arabic and Turkish darbuka are essential instruments in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean music. Whether you are a professional musician or simply a fan of this type of music, understanding the differences between these two types of darbuka can help you appreciate their unique sounds and styles.
Types of Darbuka
The darbuka is a type of frame drum that is commonly used in Middle Eastern music. It is typically played with the hands and produces a deep, resonant sound. There are several different types of darbuka, each with its own unique characteristics and features. In this section, we will explore the various types of darbuka and their differences.
- Arabic Darbuka
The Arabic darbuka is the most commonly known type of darbuka. It is typically made from clay or copper and has a round, shallow shape. The head of the drum is made from goat or sheep skin, and the drum produces a deep, low-pitched sound. The Arabic darbuka is commonly used in Arabic music and is often featured in belly dance performances.
- Turkish Darbuka
The Turkish darbuka is similar to the Arabic darbuka, but it has a slightly different shape and is made from different materials. The Turkish darbuka is typically made from wood or metal and has a deeper, more pronounced shape. The head of the drum is also made from goat or sheep skin, but it is thicker and produces a higher-pitched sound. The Turkish darbuka is commonly used in Turkish music and is often featured in Turkish folk dances.
- Israeli Darbuka
The Israeli darbuka is a type of darbuka that is unique to the country of Israel. It is typically made from metal and has a shallow, bowl-like shape. The head of the drum is made from goat or sheep skin, but it is thinner than the heads of the Arabic and Turkish darbuka. The Israeli darbuka produces a high-pitched sound and is commonly used in Israeli music and dance.
- Egyptian Darbuka
The Egyptian darbuka is similar to the Arabic darbuka, but it has a slightly different shape and is made from different materials. The Egyptian darbuka is typically made from copper and has a shallow, round shape. The head of the drum is made from goat or sheep skin, but it is thicker than the head of the Arabic darbuka. The Egyptian darbuka produces a deep, low-pitched sound and is commonly used in Egyptian music and dance.
In conclusion, there are several different types of darbuka, each with its own unique characteristics and features. The Arabic darbuka, Turkish darbuka, Israeli darbuka, and Egyptian darbuka are just a few examples of the many types of darbuka that exist. Understanding the differences between these types of darbuka can help you choose the right one for your musical needs.
Arabic Darbuka
Materials Used
The construction of an Arabic darbuka involves the use of specific materials that contribute to its unique sound and durability. The following are the most commonly used materials in the making of an Arabic darbuka:
- Head: The head of an Arabic darbuka is typically made from a synthetic material such as plastic or a petroleum-based product like celluloid. This material is chosen for its ability to maintain a taut skin that produces a clear and resonant sound when struck with the hand or a drumstick.
- Body: The body of an Arabic darbuka is made from a variety of materials, including wood, metal, or a combination of both. Wooden bodies are commonly made from woods such as oak, maple, or birch, while metal bodies may be constructed from brass, aluminum, or a combination of metals.
- Rims: The rims of an Arabic darbuka are often made from a combination of wood and metal, with the wood providing a soft and flexible surface for the head to be attached to and the metal providing additional durability and stability.
- Fittings: The fittings on an Arabic darbuka, such as the tuning screws and clamps, are typically made from metal to ensure they can withstand the tension of the head and maintain the darbuka’s pitch.
It is important to note that while the materials used in the construction of an Arabic darbuka are generally consistent, there can be variations in the specific types and qualities of these materials depending on the region and craftsman building the instrument. These variations can have a significant impact on the sound and performance of the darbuka.
Design and Construction
The design and construction of Arabic darbuka vary from region to region, reflecting the unique cultural influences of each area. In general, Arabic darbuka are typically made from clay, ceramic, or copper, and have a goblet-shaped body with a single or double-headed design.
One of the key features of Arabic darbuka is the use of a synthetic or natural goat skin head, which is stretched over the top of the body and tensioned using a tuning key. This design allows for a wide range of tonal qualities, from deep and bassy to high and bright.
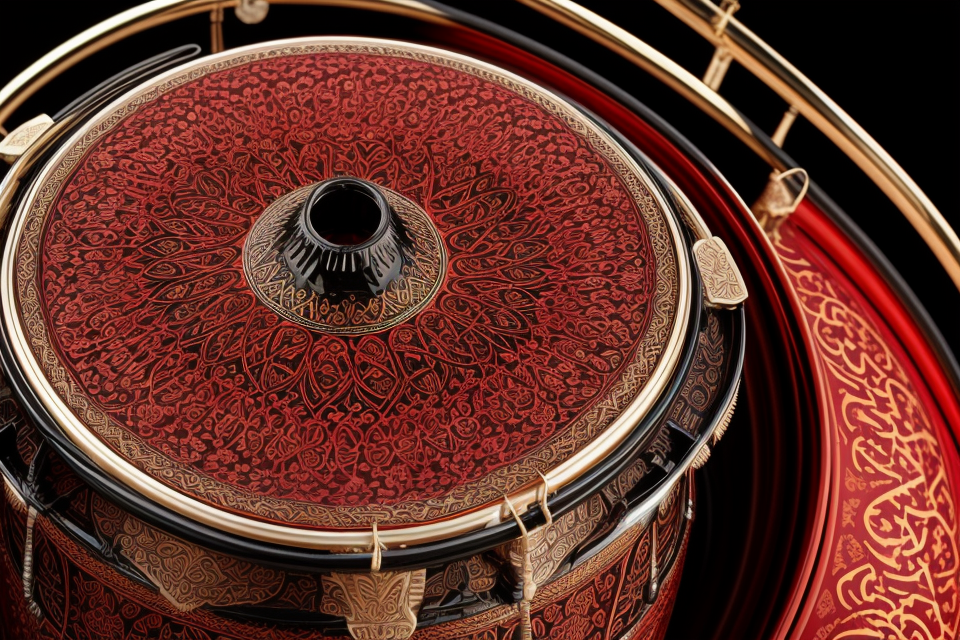
Another important aspect of Arabic darbuka design is the addition of decorative elements, such as geometric patterns, Arabic calligraphy, or intricate designs etched into the body of the instrument. These decorations not only add visual appeal but also serve to distinguish one darbuka maker from another.
Overall, the design and construction of Arabic darbuka reflect a rich cultural heritage and a deep understanding of the instrument’s potential for musical expression. Whether crafted by hand or produced on a larger scale, each darbuka is a unique blend of artistry and functionality, reflecting the skills and creativity of its maker.
Sound and Tone
Overview of Sound and Tone in Arabic Darbuka
In Arabic darbuka, the sound and tone play a crucial role in producing a distinct and captivating rhythm. The instrument’s sound is primarily characterized by its deep, resonant bass and high-pitched tonal qualities. The tonal qualities of Arabic darbuka are influenced by the instrument’s shape, size, and material, as well as the playing technique employed by the performer.
Bass Tone
The bass tone in Arabic darbuka is generated by the vibration of the drumhead against the rim. This vibration produces a deep, resonant sound that is characteristic of the instrument. The bass tone is responsible for providing the foundation of the rhythm and serves as the backbone of the music. It is important for the performer to control the bass tone, as it can greatly affect the overall sound and feel of the music.
Snare Tone
The snare tone in Arabic darbuka is produced by the snare wire, which is tightened around the edge of the drumhead. The snare wire is struck by the player’s fingers or a beater, creating a sharp, high-pitched sound that adds contrast and texture to the music. The snare tone is an essential element of Arabic darbuka, as it provides a distinct and dynamic rhythmic element that adds energy and excitement to the music.
Tonal Quality
The tonal quality of Arabic darbuka is influenced by various factors, including the size and shape of the instrument, the material used to construct it, and the playing technique employed by the performer. The tonal quality can vary greatly between different darbukas, and even between different parts of the same instrument. For example, the tonal quality of the bass and snare tones can vary significantly, depending on the specific construction and design of the darbuka.
Importance of Sound and Tone in Arabic Darbuka
The sound and tone of Arabic darbuka are critical elements that contribute to the instrument’s unique sound and character. The deep, resonant bass tone and sharp, high-pitched snare tone work together to create a rich and dynamic rhythmic texture that is essential to the music. Understanding the role of sound and tone in Arabic darbuka is crucial for performers, as it enables them to produce a high-quality, authentic sound that is true to the traditional style of the music.
Turkish Darbuka
Traditional Materials
In Turkey, the traditional darbuka is made from goat skin or cowhide. The goat skin is preferred for its tighter and more focused sound, while the cowhide is softer and produces a warmer tone. The skins are carefully selected for their thickness, texture, and durability to ensure a high-quality sound and long-lasting instrument.
Modern Materials
With the evolution of darbuka-making, modern materials have also been introduced in Turkey. Some drummers opt for synthetic skins, such as those made from polyester or PVC, which are more affordable and easier to maintain. These synthetic skins are designed to mimic the natural materials and can produce a similar sound and feel.
Additionally, some Turkish darbuka makers experiment with combining different materials to create unique sounds. For example, using a combination of goat skin and cowhide can create a darbuka with a richer and more complex tone. Experimenting with different materials and designs allows Turkish darbuka makers to push the boundaries of the instrument and create new sounds for drummers to explore.
Materials Used
The construction of a Turkish darbuka typically involves the use of various materials to create its distinctive shape and sound. One of the most commonly used materials is goat skin, which is stretched over a wooden or plastic frame to create the drumhead. Other materials used in the construction of Turkish darbuka include metal, wood, and various synthetic materials.
Drumhead Design
The drumhead of a Turkish darbuka is typically made from goat skin, which is stretched over a wooden or plastic frame. The skin is often treated with a special mixture of oils and waxes to enhance its durability and sound quality. Some Turkish darbuka players also prefer to use synthetic drumheads, which are less prone to stretching or tearing and can produce a more consistent sound.
Body Shape and Size
The body of a Turkish darbuka is typically cylindrical in shape and made from wood or plastic. The diameter of the drum can vary depending on the specific model, with larger drums producing a deeper and more resonant sound. The body of the Turkish darbuka is also typically fitted with a set of metal or plastic jingles, which are designed to create a distinctive rattling sound when the drum is played.
Features and Accessories
Many Turkish darbuka players also prefer to use a range of accessories and features to customize their instrument and enhance its sound quality. These can include special tuning keys, drumsticks, and stands, as well as a variety of protective cases and covers to keep the drum safe and protected when not in use. Some Turkish darbuka players also prefer to use a range of electronic effects and amplifiers to enhance the sound of their instrument and create a more dynamic and expressive performance.
When it comes to the sound and tone of the Turkish darbuka, there are several key differences compared to the Arabic darbuka. One of the most notable differences is the tone of the instrument. While the Arabic darbuka is known for its bright and sharp tones, the Turkish darbuka has a warmer and more mellow sound. This is due to the use of different materials in the construction of the instrument, as well as the shape and size of the darbuka.
Another difference between the two is the way in which the sound is produced. In Arabic darbuka, the sound is primarily produced by striking the head of the instrument with the fingers or a stick. In contrast, the Turkish darbuka has a more complex mechanism for producing sound, involving the use of a specialized spoon-shaped stick, called a “spoonk” or “riq” to produce a variety of different sounds.
Additionally, the Turkish darbuka is also known for its unique ability to produce a “wah” sound, which is achieved by opening and closing the sound hole on the side of the instrument while playing. This “wah” sound is not present in the Arabic darbuka and is one of the defining characteristics of the Turkish darbuka’s sound.
Lastly, the Turkish darbuka also has a unique way of tuning the instrument. Unlike the Arabic darbuka, which is typically tuned to a specific scale, the Turkish darbuka can be tuned to a variety of different scales, allowing the player to customize the instrument to their specific needs.
Overall, the sound and tone of the Turkish darbuka is distinct and different from the Arabic darbuka, with its warmer and mellow sound, unique mechanism for producing sound, the ability to produce a “wah” sound and the unique way of tuning the instrument.
Comparing Arabic and Turkish Darbuka
The choice of materials used in the construction of Arabic and Turkish darbuka drums can significantly impact their sound quality and overall performance. While both types of darbuka share some similarities in terms of the materials used, there are also notable differences.
Arabic Darbuka
Traditional Arabic darbuka drums are typically made from a combination of goat skin and solid wood, such as sycamore or mulberry. The goat skin is stretched tightly over the wooden frame, creating a resonant surface that amplifies the sound of the drum. The wooden body provides a hollow cavity that allows the sound to reverberate and enhance the overall tonal quality.
Turkish Darbuka
Turkish darbuka drums, on the other hand, are typically made from a single piece of wood, such as mulberry or oak. The wood is carved into a cylindrical shape, with a small opening at the top for the goat skin to be stretched over. The body of the drum is then hollowed out, creating a cavity that enhances the resonance of the drumhead.
While both Arabic and Turkish darbuka drums use goat skin for their drumheads, there are some differences in the way the skin is prepared and attached to the drum. In Arabic darbuka, the skin is often treated with a mixture of olive oil and salt, which helps to soften and toughen the skin, resulting in a clearer and more resonant sound. In Turkish darbuka, the skin is typically treated with a mixture of oil and wax, which gives the drumhead a more muted and slightly hazy tone.
Overall, the choice of materials used in the construction of Arabic and Turkish darbuka drums can have a significant impact on their sound quality and overall performance. By understanding these differences, players can make informed decisions when selecting a darbuka drum that best suits their needs and preferences.
The design and construction of Arabic and Turkish darbuka have distinct differences that set them apart from one another. While both instruments share some similarities, such as the use of goat skin for the drumhead and the presence of a wooden frame, the way in which they are constructed and the materials used can affect their sound and playability.
One of the primary differences between Arabic and Turkish darbuka is the materials used in their construction. Arabic darbuka are typically made from clay or terracotta, which gives them a unique sound and feel. The clay used in Arabic darbuka is often mixed with water and other materials to achieve the desired consistency, and the drum is then fired in a kiln to harden the clay and create a durable instrument.
On the other hand, Turkish darbuka are made from a variety of materials, including clay, wood, and metal. The most common type of Turkish darbuka is made from a wooden frame covered with goat skin, similar to Arabic darbuka. However, some Turkish darbuka are also made from clay, and these instruments are often larger and have a different sound than their Arabic counterparts.
Design and Shape
Another difference between Arabic and Turkish darbuka is their design and shape. Arabic darbuka are typically round or slightly curved, with a single drumhead and a small opening at the bottom for the player to hold the instrument. The design of Arabic darbuka is meant to create a balanced and controlled sound, with the player able to adjust the tone and volume by adjusting the position of the drumhead.
Turkish darbuka, on the other hand, come in a variety of shapes and sizes, from small and round to large and rectangular. Some Turkish darbuka have multiple drumheads, which allows the player to create a more complex and layered sound. The design of Turkish darbuka is meant to be more expressive and dynamic than Arabic darbuka, with the player able to use different techniques to create a wide range of sounds.
Sound and Playability
The sound and playability of Arabic and Turkish darbuka are also distinct from one another. Arabic darbuka are known for their warm and mellow sound, with a strong bass and a clear, crisp attack. The design of Arabic darbuka allows for a wide range of dynamics, from soft and subtle to loud and powerful.
Turkish darbuka, on the other hand, have a brighter and more resonant sound, with a strong midrange and a more aggressive attack. The design of Turkish darbuka allows for a wide range of techniques, from subtle rimshots to loud and powerful strokes. The sound and playability of Turkish darbuka are designed to be more expressive and dynamic than Arabic darbuka, with the player able to create a wide range of sounds and rhythms.
In conclusion, the design and construction of Arabic and Turkish darbuka have distinct differences that set them apart from one another. While both instruments share some similarities, such as the use of goat skin for the drumhead and the presence of a wooden frame, the materials used, design and shape, and sound and playability of each instrument are unique and reflect the different musical traditions and styles in which they are used.
The sound and tone of Arabic and Turkish darbuka are two of the most noticeable differences between the two styles of playing. While both styles use the same basic technique of playing with the fingers, the way the darbuka is struck and the resulting sound can vary significantly.
Sound
The sound of the Arabic darbuka is generally considered to be deeper and more resonant than the Turkish darbuka. This is due to the shape of the drum, which is typically longer and narrower than the Turkish darbuka. The sound is also characterized by a strong bass note and a distinctive “snap” on the backbeat.
Tone
The tone of the Arabic darbuka is often described as being more mellow and melodic than the Turkish darbuka. This is because the Arabic darbuka is typically played with a softer touch, which results in a more subtle and nuanced sound. In contrast, the Turkish darbuka is often played with a harder hit, which results in a more aggressive and upfront sound.
It’s worth noting that the tone of the darbuka can also be influenced by the size of the drum and the thickness of the skin. For example, a larger darbuka will generally have a deeper tone, while a smaller darbuka will have a higher pitch. Similarly, a thicker skin will produce a more mellow sound, while a thinner skin will produce a sharper tone.
Playing Techniques
The way the darbuka is played can also affect the sound and tone. For example, the Arabic style of playing often emphasizes a smooth and flowing technique, with a focus on creating a consistent and even rhythm. In contrast, the Turkish style of playing often emphasizes a more aggressive and dynamic approach, with a focus on creating a driving and energetic beat.
Overall, the sound and tone of the Arabic and Turkish darbuka are two of the most important factors to consider when choosing between the two styles. Whether you prefer a deeper and more resonant sound or a more mellow and melodic tone will depend on your personal preference and the style of music you plan to play.
Playing Techniques
Differences in Rhythm and Groove
One of the primary differences between Arabic and Turkish darbuka playing techniques is the rhythm and groove. Arabic darbuka music tends to focus on a more complex rhythmic structure, with intricate patterns and variations that are characteristic of Middle Eastern music. In contrast, Turkish darbuka music tends to emphasize a more straightforward rhythm, often featuring a steady beat and simple grooves that drive the music forward.
Striking Techniques
Another key difference in playing techniques between Arabic and Turkish darbuka is the striking technique. Arabic darbuka players often use a technique called “RIQ” or “Riqbiq,” which involves striking the skin with the fingers in a rolling motion. This technique produces a unique sound that is essential to the rhythmic structure of Arabic darbuka music. In contrast, Turkish darbuka players often use a technique called “Saglic,” which involves striking the skin with the fingertips in a more staccato manner. This technique produces a different sound that is better suited to the simpler rhythms of Turkish darbuka music.
Tone and Timbre
Finally, there are differences in the tone and timbre of the darbuka between Arabic and Turkish music. Arabic darbuka is often associated with a deep, resonant sound that is rich in overtones, while Turkish darbuka tends to have a brighter, more trebly sound. This difference in tone can be attributed to the size and shape of the darbuka, as well as the materials used to construct it.
In conclusion, the differences in playing techniques between Arabic and Turkish darbuka are significant and reflect the unique rhythmic and musical characteristics of each tradition. By understanding these differences, players can develop a deeper appreciation for the diverse sounds and styles of darbuka music.
Popular Music Styles
The darbuka, a traditional Middle Eastern percussion instrument, has played a significant role in both Arabic and Turkish music for centuries. Although the instrument itself is the same, the way it is played and the styles of music it is used in can differ significantly between the two regions. In this section, we will explore the popular music styles in which Arabic and Turkish darbuka are used.
Arabic Music
Arabic music is a rich and diverse musical tradition that has evolved over centuries. The darbuka is a central instrument in many Arabic music genres, including classical Arabic music, traditional Bedouin music, and contemporary Arabic pop music.
One of the most well-known styles of Arabic music is classical Arabic music, which originated in the medieval period and is still performed today. This style of music is characterized by its complex rhythms and intricate melodies, and the darbuka plays a crucial role in maintaining the rhythm and providing a foundation for the other instruments.
Traditional Bedouin music, on the other hand, is a more folk-based style of music that is typically performed at social gatherings and celebrations. The darbuka is often used in this style of music to provide a lively beat and to add energy to the performance.
In contemporary Arabic pop music, the darbuka is also commonly used, providing a distinctive Middle Eastern sound to many popular songs.
Turkish Music
Turkish music is a diverse and vibrant musical tradition that has been influenced by a variety of cultural traditions, including those of the Ottoman Empire and the various ethnic groups that make up modern-day Turkey. The darbuka is a popular instrument in many styles of Turkish music, including traditional Turkish folk music and contemporary Turkish pop music.
In traditional Turkish folk music, the darbuka is often used to provide a driving rhythm and to add energy to the performance. This style of music is characterized by its lively melodies and complex rhythms, and the darbuka is an essential instrument in creating this distinctive sound.
In contemporary Turkish pop music, the darbuka is also commonly used, providing a distinctive Middle Eastern sound to many popular songs. The instrument is often used in conjunction with other instruments, such as the oud and the ney, to create a rich and varied sound.
Overall, while the darbuka is used in a similar way in both Arabic and Turkish music, the styles of music in which it is used can differ significantly. Whether playing traditional classical music or contemporary pop, the darbuka remains an essential instrument in Middle Eastern music.
Cultural Significance
Arabic and Turkish darbuka have distinct cultural significance in their respective regions. While both drums are similar in their appearance and function, their cultural implications vary due to their historical and geographical origins.
Arabic darbuka holds significant cultural value in the Middle East, particularly in countries such as Egypt, Sudan, and Morocco. It is deeply rooted in the region’s rich musical heritage and has been a part of Arab culture for centuries. Arabic darbuka is commonly used in traditional Arabic music, including belly dance music, and is considered an essential instrument in many Arabic ensembles.
Turkish darbuka has a prominent place in Turkish culture, where it is known as the “darbuka.” It is a crucial instrument in Turkish folk music and is also used in traditional belly dance music. The darbuka has been a part of Turkish culture for centuries and is closely associated with the country’s musical heritage.
While both Arabic and Turkish darbuka have cultural significance in their respective regions, their cultural implications go beyond their musical uses. In many Arab and Turkish communities, the darbuka is considered a symbol of cultural identity and pride. It is often used in cultural celebrations and ceremonies, such as weddings and festivals, and is passed down from generation to generation as a cultural heirloom.
Overall, the cultural significance of Arabic and Turkish darbuka highlights the importance of music and cultural traditions in shaping identity and preserving cultural heritage.
Popular Artists
While Arabic and Turkish darbuka may have similar origins and share some similarities in terms of their construction and playing techniques, there are also some notable differences between the two. One of the most obvious differences is in the popular artists who have made a name for themselves using these drums.
In Arabic music, the darbuka is often used to provide a steady rhythm and add a percussive element to the music. Some of the most well-known Arabic musicians who have used the darbuka in their music include the late legendary Egyptian singer Umm Kulthum, the renowned oud player and composer Naseer Shamma, and the popular Lebanese singer and composer Tania Saleh.
In Turkish music, the darbuka is also a key instrument, and it is often used to provide a driving beat and add energy to the music. Some of the most celebrated Turkish musicians who have made the darbuka a central part of their sound include the late legendary Turkish composer and singer Sevgi Kasapoğlu, the popular Turkish folk singer Hidayet Turkoglu, and the acclaimed Turkish rock band Yüksek Sadakat.
It is worth noting that while the darbuka is an essential instrument in both Arabic and Turkish music, the way it is played and incorporated into the music can vary significantly between the two styles.
Recommendations for Darbuka Enthusiasts
When it comes to choosing between an Arabic and a Turkish darbuka, there are a few key factors to consider as a darbuka enthusiast. Here are some recommendations to help you make an informed decision:
Style and Sound
- Consider the style of music you want to play and the sound you are looking for. Arabic darbuka tend to have a more traditional, earthy sound, while Turkish darbuka often have a more modern and bright tone.
- Think about the size and weight of the darbuka. Arabic darbuka tend to be larger and heavier, while Turkish darbuka are usually smaller and lighter.
-
Consider the material of the darbuka. Arabic darbuka are often made from clay or ceramic, while Turkish darbuka are typically made from aluminum or other metals.
-
Keep in mind the playing techniques used in the music you want to play. Arabic darbuka playing often involves a lot of slapping and hitting the drum head, while Turkish darbuka playing often involves more rolling and sliding.
- Think about the tuning of the darbuka. Arabic darbuka are often tuned to a lower pitch, while Turkish darbuka are often tuned to a higher pitch.
Budget
- Finally, consider your budget. Arabic darbuka tend to be more expensive than Turkish darbuka, due to the materials and craftsmanship involved in their production.
Overall, the choice between an Arabic and a Turkish darbuka will depend on your personal preferences and the music you want to play. By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision and find the perfect darbuka for your needs.
FAQs
1. What is a darbuka?
A darbuka is a type of percussion instrument that is commonly used in Middle Eastern music. It is typically a clay pot with a skin head, and is played by striking the skin with the hands or with a drumstick.
2. What is the difference between Arabic and Turkish darbuka?
The main difference between Arabic and Turkish darbuka is in their design and playing style. Arabic darbuka has a more rounded shape and a narrower body, while Turkish darbuka is generally more cylindrical in shape and has a wider body. Additionally, Arabic darbuka tends to have a deeper sound and is played with a more subtle technique, while Turkish darbuka has a higher pitch and is played with a more aggressive technique.
3. What is the origin of the darbuka?
The exact origin of the darbuka is unclear, but it is believed to have originated in the Middle East, possibly in Egypt or Iraq. It has been used in Middle Eastern music for centuries and has become an essential instrument in many genres of music, including belly dance music and traditional folk music.
4. How is a darbuka played?
A darbuka is played by striking the skin head with the hands or with a drumstick. The player can create different sounds by using different parts of the skin head and by varying the strength and angle of their strikes. They can also use different techniques such as rimshots, rolls, and accents to add variety to their playing.
5. Can I learn to play a darbuka?
Yes, anyone can learn to play a darbuka. There are many resources available online, including tutorials, videos, and lessons, that can help you learn the basics of playing the instrument. It’s also a good idea to take lessons from a professional musician or teacher to get personalized instruction and feedback.
6. What types of music is a darbuka commonly used in?
A darbuka is commonly used in Middle Eastern music, including belly dance music, traditional folk music, and pop music. It is also used in other genres of music, such as jazz and rock, as a way to add a Middle Eastern flavor to the music.
7. What are the different parts of a darbuka?
A darbuka typically has two main parts: the body and the skin head. The body is usually made of clay or wood and has a round or cylindrical shape. The skin head is usually made of goat or sheep skin and is stretched over the body of the darbuka. The darbuka also has a hole in the center, which is used to adjust the tension of the skin head and to create different sounds.

